Data Structures
Introduction:
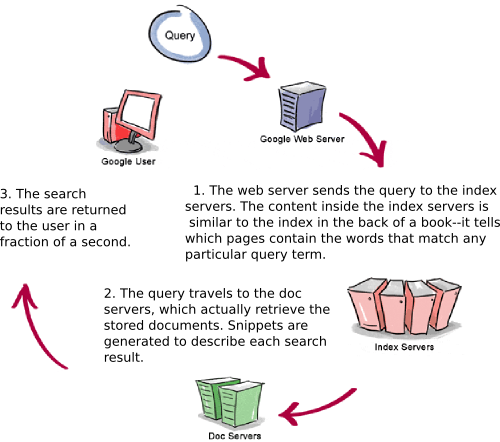
Let’s see how Google processes a query.
Definition:
In computer science, a data structure is a
particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be
used efficiently
Types of Data
Structures:
1. Linear
Data Structures
·
Data manage in linear fashion or linear format
·
Eg. Array, Linked list, stack
and queue
2. Non-Linear Data Structures
·
Data manage in non-linear
format
·
Eg. Tree and
Graph
Classification
of Data Structures:
·
Primitive / Non-Primitive Data
Structures
·
Homogeneous / Heterogeneous
Data Structures
·
Static / Dynamic Data
Structures
·
Linear / Non-Linear Data
Structures
Primitive/Non-Primitive
Data Structures
•Primitive data structures are the basic data structures that can be
directly operated upon machine instructions.
Eg. int, char,
float, double etc.
•Non-primitive data structure are the abstract data structure that are derived from the primitive data structure.
Eg. structure,
union , array etc
Homogeneous/Hetrogeneous
Data Structures
•In a data structure if all the elements are of same data type, it is
called homogeneous data structure.
Eg. Integer array
•A hetrogeneous data structure is the one which can contain data
elements of different data types.
Eg. Structure
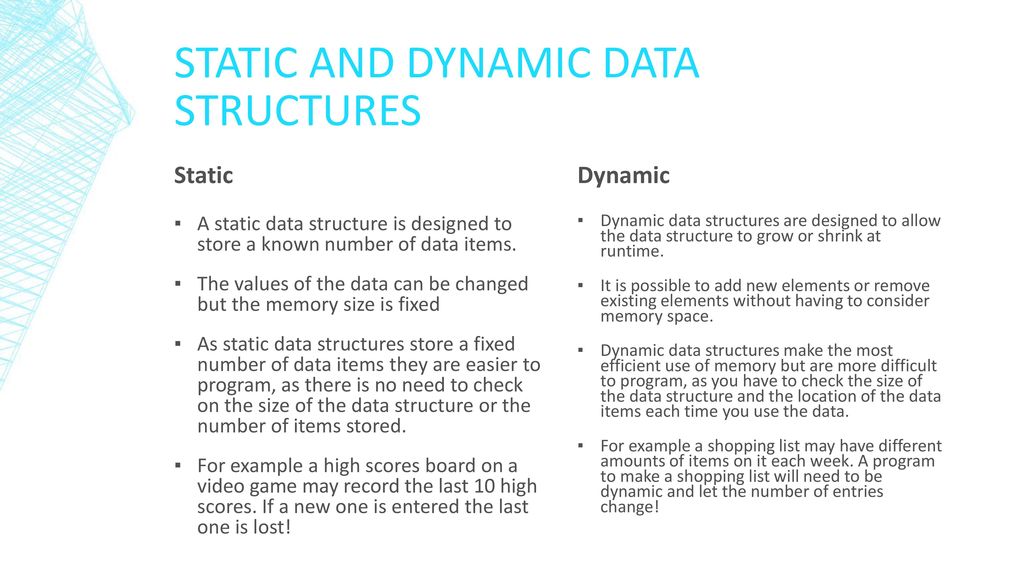
Static / Dynamic Data Structures
· Static data structure follows static memory
allocation.
· Dynamic data structure follows dynamic
memory allocation.
· Static memory allocation: The compiler allocates the required memory
space for a declared variable. By using the address of operator, the reserved
address is obtained and this address may be assigned to a pointer variable.
Since most of the declared variable have static memory is assigned during
compilation time.
· Dynamic memory allocation: It uses functions such as malloc( ) or
calloc( ) to get memory dynamically. If these functions are used to get memory
dynamically and the values returned by these functions are assigned to pointer
variables, such assignments are known as dynamic memory allocation. memory is
assigned during run time
Linear /
Non-Linear Data Structures
Linear Data Structures
· Data manage in linear fashion or linear format
· Eg. Array, Linked list, stack and queue
Non-Linear Data
Structures
· Data manage in non-linear format
· Eg.
Tree and Graph
Array:
· An array is defined as a set of finite
number of homogeneous elements or data items. Or
· An array is the collection of elements of
same data type that are stored contiguous in memory.
· It means an array can contain one type of
data only, either all integers, all floating numbers or all characters.
· Declaration of array in C language is given
by
int a[10] ;
where int specifies the data type or
types of elements that an array stores. “a” is the name of an array and the
number specified inside square bracket ( [ ] ) is the number of elements an
array can store , this is also called as the size or length of an array.
Linked list:
· A linked list can be defined as a
collection of variable numbers of data items.
· Linked list are the most commonly used non-primitive
data structure.
· An element (or node) of list must contain
at least two fields; one for storing data or information part, and other for
storing address or link of next node.
· For storing an address we have to use a
special type of variable or data structure known as pointer (used in
C-language).
· Hence the second field of any node must be
of pointer type.
info[100]=11
link[180]=210
link[330]=NULL
Exercise:
info[start]= 11
info[210]= 28
link[300]= 330
link[ link[180] ]=
280
info[link[start]]=
19
Stack:
· A stack is also an ordered collection of
elements like an array, but it has a special feature that deletion and
insertion of element can be done from one end, called the top of the stack
(TOP).
· Due to this property it is also called as
Last in First out [LIFO] in data structure.
· It could be thought of just like a stack of
plates placed on table in a party, a guest always takes off a fresh plate from
the top of the stack, and the new plates are placed on to the stack.
· A stack is a non-primitive data structure.
· When an element is inserted into a stack or
removed from the stack, its base remains fixed where as the top of the stack
changes.
· Insertion of an element into a stack is
known as PUSH.
· Deletion from an element from the stack is
known as POP.
· TOP value indicates an index (in case of an
array) or address (in case of linked list) where an incoming element will be
inserted.
· The stack can be implemented
a) Using Array (Static Implementation)
b) Using Pointer (Linked List; Dynamic implementation)
Queue:
· Queues are the first in first out data
structure [FIFO].
· In a queue new elements are added
(inserted) to the queue from one end called as REAR end and the elements are
always removed (or deleted) from the other end is called as FRONT end.
· The people standing in a railway
reservation counter or row are an example of queue. Each new person comes and
stand at the end of row (Rear end of the queue) , and the person getting
reservation get out of the row from the front end.
· The Queue can be implemented
a) Using Array (Static
Implementation)
b) Using Pointer (Linked List;
Dynamic implementation)
Tree:
· A tree can be defined as finite set of data
items (nodes).
· Tree is a non-linear type of data structure
in which data items are arranged or stored in a sorted order.
· Trees represents the hierarchical
relationship between various nodes.
Property of a
tree:
· In a tree, there is a special data item at
the top of the hierarchy called the root of the tree.
· Remaining items are partitioned into
mutually exclusive (disjoint) subset, each of which is itself a tree which is
called the sub-tree.
· The trees always grows in height towards
bottom in data structure.
Example:
Graph:
· A graph is a mathematical non-linear data
structure capable of representing many kinds of physical structure.
· Example: Geography, chemistry, Engg.
Science and so on.
· A graph G(V,E) is a set of vertices ‘V’ and
a set of edges ‘E’. An edge connects a pair of vertices and many have weight
such as length, cost and so on. Vertices on the graph are shown as point or
circle and edges are drawn as arcs or line segments.
· Thus an edge can be represented as E=(V,W) where V and W are pair of vertices.
Formal definition of graphs:
· A graph G is defined as follows:
G=(V,E)
V(G): a finite, nonempty
set of vertices
E(G): a set of edges (pairs of vertices)
There are two standard ways of representing a graph G in the memory of a computer:
1)Sequential
Representation (Using Adjacency matrix A)
2)Linked List Representation
Data Structure operation:
· The data appearing in the data structures
are processed by means of certain operations. In fact, the particular data
structure that one chooses for a given situation depends largely on the
frequency with which specific operation are performed.
· The following operations are performed on
the data structures:
1) Traversing
2) Searching
3) Sorting
4) Merging
5) Insertion
6) Deletion
Traversing:
· Visit each element or node in the list at
least once.
Searching:
· The operation finds the presence of the
desired data item in the list of data items.
· It may also find the location of element that satisfy particular condition.
Sorting:
· It is the process of arranging all data
items in a data structure in a particular order say for example either in
ascending order or in descending order.
Merging:
· It is a process of combining the data items
of two different sorted list into a single sorted list.
Insertion:
· Adding a new record or data item into the
data structure
· Insertion can be in any one of the
following position:-
1) Insertion may be at beginning
2) Insertion may be at Middle
3) Insertion may be at last
· Removing or deleting a record or data item
from the data structure
· Deletion can be in any one of the following
position:-
1) Deletion may be at beginning
2) Deletion may be at Middle
3) Deletion may be at last











0 Comments